Setting Up Ingress-Nginx in a Kubernetes Cluster - Part 1

Today we’ll be installing and configuring the kubernetes-supported ingress-nginx controller via helm into a digitalocean kubernetes cluster (DOKS). Which will use nginx as a reverse proxy and load balancer.
This will be the first in a two-part series about configuring ingress. This part will focus on just getting it setup as an http connection and the next will focus on setting up and using a secure connection with TLS certificates.
Ingress-nginx installation and configuration (http)⌗
Let’s start by adding its repository to Helm:
helm repo add ingress-nginx https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx
We are then going to pull the chart and download it locally, so we can update the values.yaml file and declaratively store it. This will download it into the folder that you are in:
helm pull ingress-nginx/ingress-nginx --untar
In the values.yaml file we are going to configure:
- The
controller.publishService.enabledvariable totrue- This is needed because only the
LoadBalancerservice will know the IP address of the automatically created Load balancer. However, some apps can only read theIngressconfiguration files. Setting this value will make the Controller publish the IP address on eachIngressresource.
- This is needed because only the
- The
controller.service.annotationsvariable to look like:
controller:
service:
annotations:
service.beta.kubernetes.io/do-loadbalancer-protocol: "http"
service.beta.kubernetes.io/do-loadbalancer-size-unit: "1"
- These are needed to create a very small, http Load Balancer in DigitalOcean
We can now install the chart:
helm install ingress-nginx . -n ingress-nginx
After a couple of minutes the pod should be running in the ingress-nginx namespace
kubectl get pods -n ingress-nginx
There shoud also be an EXTERNAL-IP address associated with the service
kubectl get service ingress-nginx-controller -n ingress-nginx
This will be the same IP as the created DigitalOcean Load Balancer.
Example app installation and configuration⌗
Once this is created, if you already have a Deployment, Service and Ingress resource for your own app, you can go ahead and deploy those. Here is an example for reference:
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: demo
name: demo
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: demo
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: demo
spec:
containers:
- image: httpd
name: httpd
ports:
- containerPort: 80
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: demo
name: demo
namespace: default
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 80
selector:
app: demo
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: demo
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
rules:
- host: <your-domain>
http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: demo
port:
number: 80
path: /
pathType: Prefix
Update the host in the Ingress resource to a domain that you own. Assuming that you are using DigitalOcean to host your domain, you can create an A record using that domain and point it to the IP address of your Load Balancer. It can either be done in the UI or via the CLI:
doctl compute domain records create <demo.example.com>
Verify that the records were created:
doctl compute domain records list <demo.example.com>
You should now be able to use curl or a web browser to test it!
curl -Li http://<your-domain>
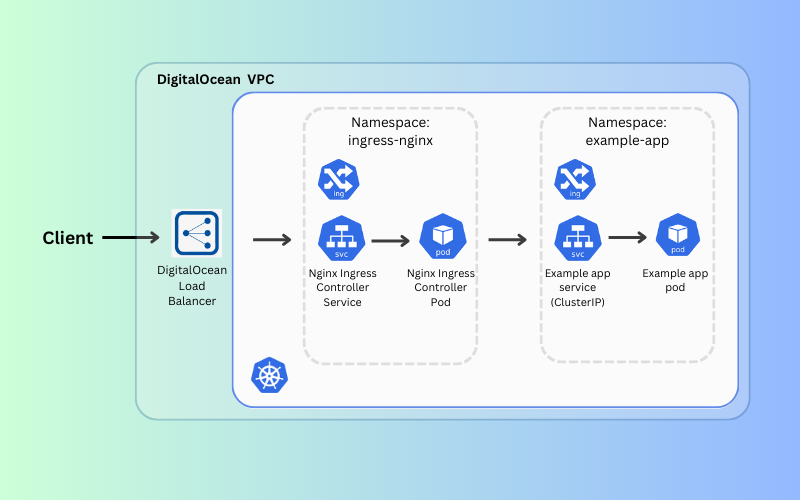
Let’s summarize what exactly happened:
- We installed the nginx ingress controller
- This consists of a Pod and a Service and is needed in order for the
Ingressresource to work- The Pod runs the Controller, which is constantly polling the
/ingressesendpoint on your API server of your cluster for possible updates to availableIngressresources- The Service is of type
LoadBalancerand becauseDigitalOceanhas a cloud-controller-manager, this automatically provisions aDigitalOceanLoad Balancer since it is responsible for watching services of this type.- We updated the values in the helm chart to allow the Controller to publish the EXTERNAL-IP address to the
Ingressresources and to add annotations to create a small, http Load Balancer in DigitalOcean- We then installed the
DeploymentandIngressresources of our example app to the cluster- Finally, we added an A record domain with the value of the host that we used in our
Ingressresource and this points to the Load balancer IP (EXTERNAL-IP)
Here is a diagram of what was completed:
If you would like to learn about setting up TLS certificates for your backend services - move onto Part 2